Did you know that you are a complex ecosystem hosting trillions of microorganisms? The microbes living in and on your body outnumber the human cells by approximately 1.3:1! These microorganisms consist of bacteria, fungi and viruses and are a mix of commensal (neutrally existing), symbiotic (mutually beneficial) and pathogenic (harmful to us) organisms and are mostly located in your gut.
While this may sound gross, without these organisms you wouldn’t be able to access the essential nutrients from the food you eat. You also wouldn’t have a proper functioning immune system and the vital communication between your cells would cease. So not a great outcome for you.
Interestingly, the human genome consists of approximately 22 000 genes – we are 99% identical to each other while the microbiome in your gut consists of 3.3 million genes and differs by 80 – 90% between individuals. Your microbiome is what makes you a special snowflake.
WHAT DO THESE BUGS DO?
The diverse organisms living in your gut perform wide-ranging functions critical to your health.
Digestion
The microorganisms in your gut break down the food you eat so that you can absorb and use the nutrients.
Regulating metabolism
Bacteria ferments dietary fiber to produce short-chain fatty acids which are beneficial energy sources and essential for regulating metabolism.
Synthesizing and absorbing vitamins and minerals
Gut bacteria play a role in increasing the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, E, D and K and synthesizing vitamins like B and K.
Fermenting protein
The BCAA’s required for gains are made by the bacteria fermenting your chicken breast and rib-eye steak.
Maintaining the integrity of your gut barrier and blood-brain barrier
Foreign particles and pathogens are not welcome in your bloodstream and brain for obvious reasons and your gut bacteria have an influence on the permeability of certain epithelial cells and barriers located throughout your body. These epithelial cells keep the bad stuff out of your brain and bloodstream.
Modulating the immune system
Your immune system is kept in delicate balance by the gut bacteria which keeps the various immune cell populations in check and modulates their activity.
These are only some of the functions on which your gut microbiome has influence. The study of the microbiome is in its infancy and we are only just beginning to understand how important it is to nurture a healthy and diverse ecosystem in our gut!
HOW CAN I ENSURE A HEALTHY GUT MICROBIOME?
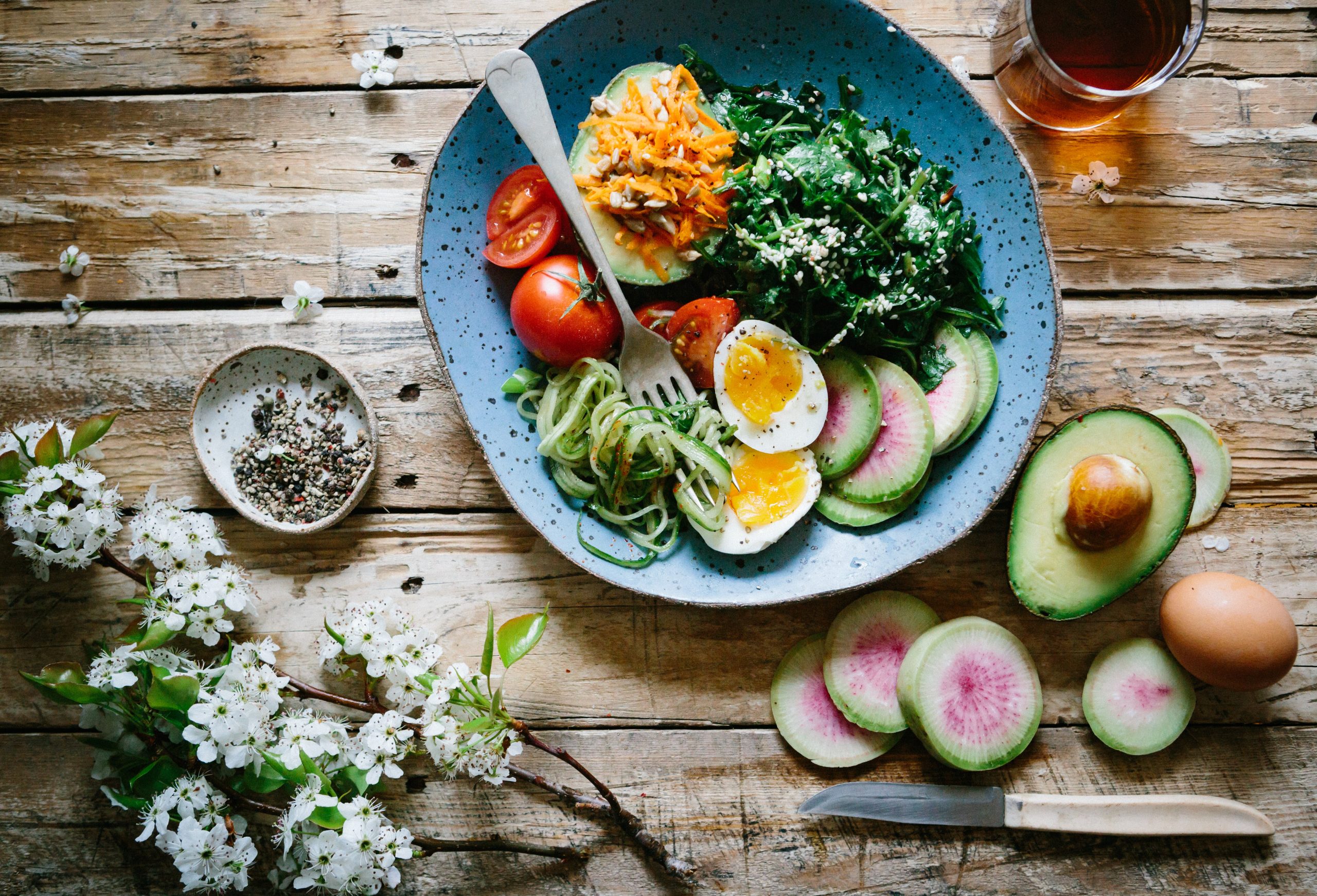
Diet has the biggest influence on the composition of your gut microbiome. A diet rich in fresh fruit and vegetables can support the growth of beneficial microorganisms. Adequate fiber and fish oil will also support a diverse and healthy microbiome.
Lifestyle also plays an important role. Overtraining, not getting enough quality sleep and too much stress negatively impacts the microbiome and causes too many of the pathogenic organisms to take hold.
Too much sugar is also problematic and dairy, grains, alcohol and legumes can also promote the growth of the wrong kinds of bacteria.
So a balanced diet that includes enough fiber, plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables and adequate protein intake will help your gut microbiome (and you) flourish. Taking care of chronic and excess stress, optimizing your environment and getting enough good-quality exercise will also help – all the things we encourage you to look after at CFJ Lifestyle Fitness!
By: Coach Lisa